A significant impact of the digital age on business is the increased reliance that companies are starting to place on their technology capabilities. With that comes a need for Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Business Analysts who bridge the gap between the needs of the business and the technology available to ensure that companies are using ICT in a way that will meet their strategic goals.
This article describes the job of an ICT business analyst, including its description, the skills required, the demand for the position, career prospects, and more.
🔑 Key Highlights
- Responsibilities of an ICT Business Analyst: Their main responsibilities include obtaining and evaluating requirements, enhancing business procedures, interacting with stakeholders, developing and putting into practice technical solutions, and testing to guarantee quality.
Unlike traditional business analysts, ICT business analysts are focused on information technology. They ensure that IT systems and applications are designed to support and improve business processes. These are critical skills for digital transformation initiatives in today’s tech-heavy environment.
Key Responsibilities of an ICT Business Analyst
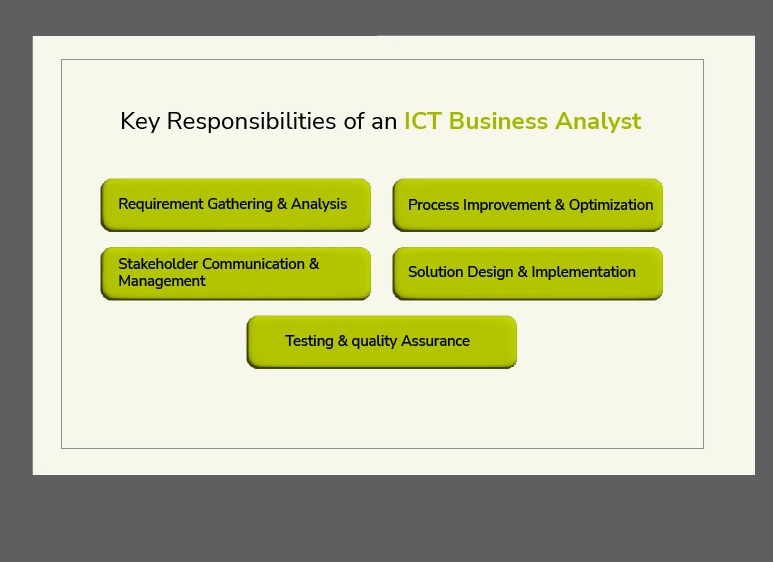
An ICT business analyst has several fundamental duties that need fulfilment.
An ICT business analyst handles a range of responsibilities that depend on both the industry sector and organisational size, along with specific project needs. An ICT business analyst has several main responsibilities to fulfil.
1. Requirement Gathering and Analysis
The principal function of an ICT business analyst is to collect business requirements for documentation and systematic analysis. I conduct research with stakeholders to understand their requirements, problems, and minimum standards. The information acquisition process of business analysts involves applying methods like interviews and surveys as well as workshops.
2. Process Improvement and Optimization
ICT business analysts review organisation processes to locate performance weaknesses before giving optimisation suggestions. The professional uses business process modelling (BPM) tools for organising workflow diagrams that reveal process slowdowns.
3. Stakeholder Communication and Management
Communication effectiveness becomes essential since ICT business analysts need to connect with three groups: business executives, IT teams and the end-users. As intermediaries, they perform dual responsibilities by changing business needs into technical specifications and technical specifications into business needs.
4. Solution Design and Implementation
The defined business requirements allow ICT business analysts to join forces with IT teams to create suitable technological solutions. Business analysts must perform software selection in addition to system development and process automation tasks and system integration to existing infrastructure components.
5. Testing and Quality Assurance
The deployment of new IT solutions depends on ICT business analysts who perform thorough testing to verify that they satisfy all business requirements. Together with quality assurance teams, they execute functional testing as well as user acceptance testing and system performance checks.
Essential Skills for an ICT Business Analyst

An ICT business analyst needs technical expertise, together with analytical and interpersonal abilities, to prosper in this field. The necessary competencies for an ICT business analyst include:
1. Technical Proficiency
The business analyst must understand how the software development life cycle (SDLC) functions.
An ICT business analyst needs to understand programming languages, which include SQL Python and Java, as well as others.
Familiarity with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and customer relationship management (CRM) software
Business analysts need to handle data analytics tools when using Power BI or Tableau software.
2. Business Acumen
A deep knowledge of business operation methods and industry-leading standards exists.
IT solutions must be developed in line with organisational business goals and objectives.
The professional has experience in both business strategy development and market analysis.
3. Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking
Someone with problem identification experience should also have the ability to find effective solutions to those problems.
The candidate should possess outstanding research abilities along with robust analytical capabilities to conduct business need assessments.
Proficiency in root cause analysis and impact assessment
4. Communication and Interpersonal Skills
The person must demonstrate superior skills in speaking and writing to effectively engage stakeholders.
Technical content conversion ability for business-related communication
Effective collaboration with cross-functional teams
5. Project Management
Knowledge of project management methodologies such as Agile and Scrum
Knowledge of how to operate tracking systems, including Jira and Trello.
A person needs competence to coordinate multiple projects and reach target dates.
6. Attention to Detail
The system requires precise documentation together with reporting output and analytical results, maintaining high accuracy levels.
The team must detect foreseeable risks alongside the creation of risk reduction procedures.
Career Path and Job Opportunities
Career Path and Job Opportunities

1. Entry-Level Positions
Most ICT business analysts enter the industry through positions such as:
- IT Support Analyst
- Junior Business Analyst
- Systems Analyst
- Data Analyst
Starting jobs in junior positions offers essential training in analysing business demands and helping IT departments as well as handling data-based decisions.
2. Mid-Level Roles
Professionals who gain experience through their work can enhance their career path towards senior positions, which include
- ICT Business Analyst
- Business Systems Analyst
- IT Consultant
- Product Manager
3. Senior and Leadership Roles
More experience along with expertise growth allows ICT business analysts to pursue roles such as senior ICT business analyst positions or become IT project managers, Chief Information Officers or business intelligence managers.
- Senior ICT Business Analyst
- IT Project Manager
- Chief Information Officer (CIO)
- Business Intelligence Manager
4. Freelancing and Consulting
Freelance business analysis consultants service companies under agreements by providing specialised consulting services. Through this path, professionals gain more flexibility and accumulate better earning potential.
Industries That Hire ICT Business Analysts
The ICT Business Analyst professional maintains active demand within different fields of business, including:
Banking and Finance: Supporting digital banking initiatives, fraud detection, and compliance solutions.
The healthcare industry requires EHR system implementation and patient data management improvement.
Retail and E-commerce: Enhancing customer experience through data-driven insights and automation.
IT networks and customer service platforms are managed by telecommunication specialists in its operations.
Government and Public Sector: Developing IT solutions for digital governance and citizen services.
Manufacturing: Implementing ERP systems for supply chain management and production tracking.
Future Trends in ICT Business Analysis
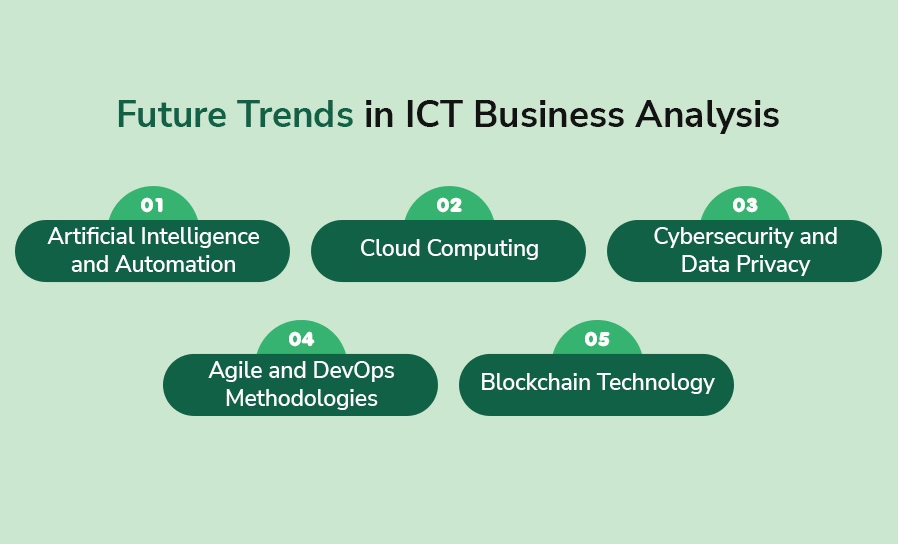
The profession of ICT business analysts transforms itself because of technological advancements. Three main developments currently influence the professional future of ICT business analysts:
1. Artificial Intelligence and Automation
Technology-powered business analytics tools bring transformative benefits to data analysis, which allows ICT business analysts to achieve faster and more accurate decisions.
2. Cloud Computing
The adoption of cloud-based IT solutions creates a rising requirement for analysts who can handle AWS Azure and Google Cloud platforms.
3. Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
Dozens of cybersecurity dangers demand that ICT business analysts verify both IT systems and adhere to security standards that include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
4. Agile and DevOps Methodologies
As software development implements Agile and DevOps methodologies, it becomes essential for ICT business analysts to learn agile development with its iterative approach.
5. Blockchain Technology
The financial sector, along with supply chain operations, is implementing blockchain networks for protected monetary exchanges, which offers new job prospects to ICT business analysts.
Conclusion
Digital networks require the essential contribution of ICT business analysts for current operational success. These experts link business aims with technological structures while making sure organisations maintain their market position and technology-driven innovation. ICT business analysts who develop appropriate skills and experience along with adaptability methods will succeed in building a successful career pathway over multiple business sectors.
Business organisations will sustain their need for skilled information as they adopt digital transformation strategies. Success in the career of ICT business analysis requires a combination of technological expertise with business problem-solving ability.
FAQS
1. How to be an ICT business analyst?
The steps are as follows:
- Education
- Gain Skills
- Certifications
- Gain Experience
- Build a Portfolio
- Network
2. What is ICT in business analysis?
ICT in business analysis refers to the use of technology to manage, process, and communicate information within a business.
3. What are the top 3 skills of a business analyst?
The top 3 skills of a business analyst are as follows:
- Analytical Thinking and Problem-Solving
- Communication and Interpersonal Skills
- Technical Proficiency
4. Is an ICT business analyst in demand in Australia?
Yes, an ICT business analyst is in demand in Australia.
5. What is the role of an ICT systems analyst?
The role of an ICT system analyst is as follows:
- Systems Analysis
- Requirements Gathering
- System Design and Development
- Testing and Validation
- Integration
- Documentation

